A cold home or a lukewarm shower can be a major source of stress, especially during a chilly winter in the North East. When a combi boiler fails, the first instinct is often to panic. However, modern central heating systems are logical machines. They use a specific sequence of operations to provide heat and hot water. Understanding how to find a fault is about using a systematic process of elimination to identify the root cause.
The Logic of Systematic Boiler Fault Finding
Diagnostics in modern combination boilers follow a strict “if/then” protocol. A combi boiler is a compact unit that heats both radiators and water on demand. Professional heating engineers track the system’s “sequence of operation” to see exactly where the cycle breaks. When a demand for heat is made, the unit must complete a series of safety and functional checks in a specific order.
If any single step is not confirmed by the internal sensors, the system will trigger a lockout and usually display a specific fault code. By identifying the exact moment the process stops, a technician can move directly to the specific boiler fault. This prevents unnecessary work and ensures the finding and repair process is targeted and effective. Beyond just restoring heat, precise diagnostics ensure your system remains as energy efficient as possible, helping homeowners stay compliant with the strict conservation standards set out in Part L of the Building Regulations.
The Diagnostic Toolkit: Investigating a Boiler Fault
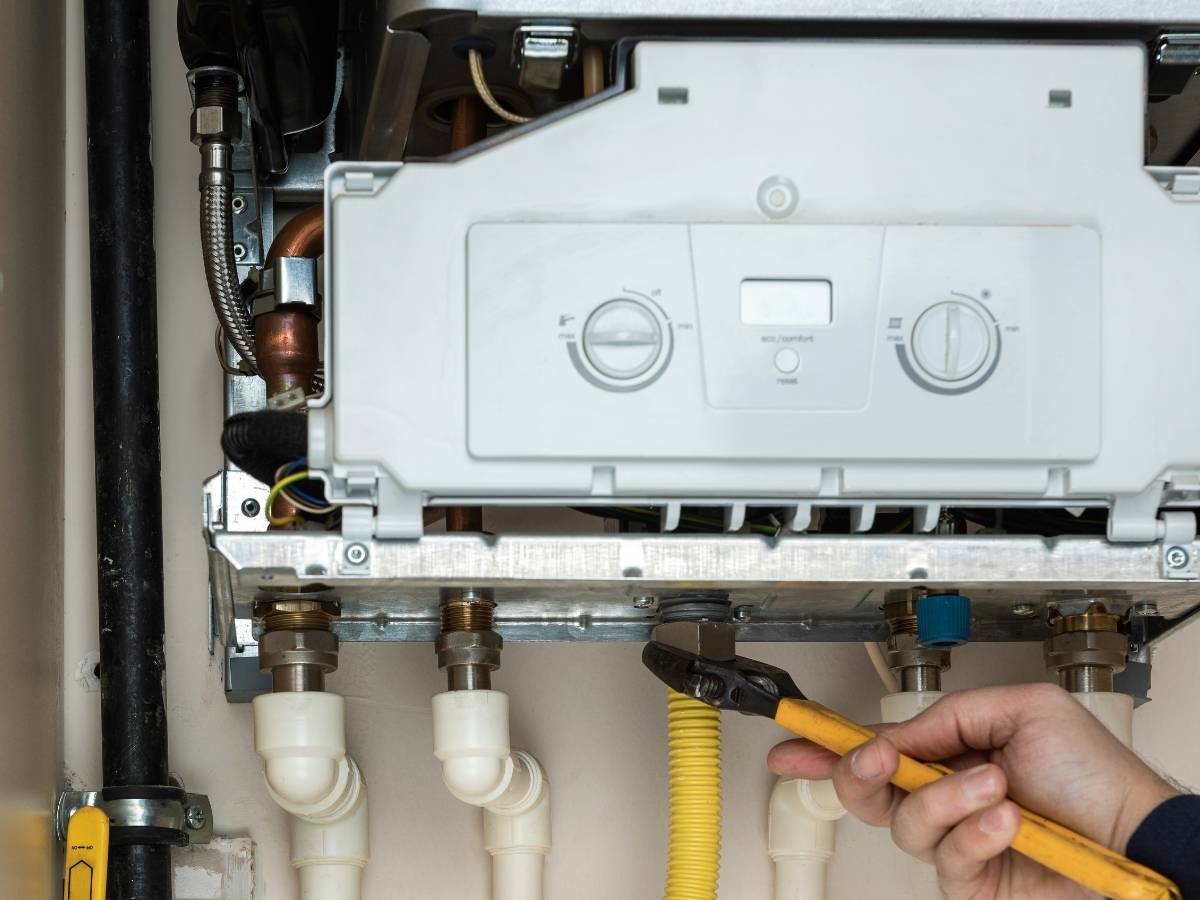
To find a fault accurately, gas engineers rely on a mix of digital data and physical tools to see what is happening inside the system.
The Digital Interface and Pressure Gauges
Most modern units are equipped with a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). Think of this as the brain of the boiler. If something goes wrong, the PCB monitors various boiler components and generates an error code. These codes provide a vital hint, such as “low water pressure” or “ignition failure.” Additionally, water pressure is the lifeblood of the system. Most models need to sit between 1.0 and 1.5 bar when cold. If the boiler pressure is too low, the system will refuse to fire up to protect the heat exchanger. Ensures the finding and repair process is targeted and effective. All work must be carried out in accordance with the Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998 to ensure the safety of your home.
Professional Testing Tools
For deeper issues, specialist equipment is used. A multimeter is essential for electrical safety checks, testing parts like sensors and fans for “continuity.” This confirms if a part is getting power but failing to act. Experts also use flue gas analysers to measure efficiency and ensure the unit is not producing dangerous levels of carbon monoxide.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Techniques
When an expert arrives at a home, they follow a set path to find the problem. This ensures no simple fixes are missed before moving on to more complex parts.
Stage 1: External and Hydraulic Checks
The process begins by verifying power and gas supplies. A tripped fuse or a lack of credit on a pre-paid meter are common culprits. Next, the water system is checked for leaks or airlocks. Air trapped in the system can stop the pump from moving water, leading to a sudden shutdown.
Stage 2: Component Logic
This is where the startup sequence is observed:
- The Fan: Must start first to clear leftover gases from the combustion chamber.
- Air Pressure Switch: Confirms the fan is creating the right vacuum.
- The Pump: Circulates water to protect the heat exchanger from melting.
- Ignition: The gas valve opens, and a spark is created to light the burner.
If the fan spins but the unit never sparks, the technician knows the issue lies between the air pressure switch and the ignition lead.
Applying Skills from a Boiler Fault Finding Course
Professional development is vital in this industry. A dedicated boiler fault finding course allows technicians to stay up to date with the latest digital diagnostic technologies across different boiler manufacturers.
Understanding Technical Course Details
When looking at the course details for professional gas training, engineers focus on learning the unique startup sequences of various UK models. Many a training centre will offer a learning programme that covers everything from basic entry requirements for new starters to advanced diagnostics for veterans. Some even offer a free trial or taster session to show how they teach complex wiring and logic. This training ensures that when they visit your home, they combine technical skill with excellent customer service to resolve your issue quickly. You can always check the official Gas Safe Register to verify an engineer’s credentials before they begin work.
Common Diagnostic Scenarios
In professional diagnostics, several scenarios appear frequently:
- Hot Water Works, But Heating Doesn’t: Usually a faulty diverter valve. This part directs hot water to either taps or radiators. If it sticks, you lose one of the two functions.
- Tepid Hot Water: Often caused by a blocked plate heat exchanger. Limescale can prevent heat from transferring effectively to your domestic water.
- Boiler Cuts Out After Firing: Typically a “flame rectification” fault where a dirty sensor fails to detect the flame, causing a safety shutdown.
Conclusion
Effective fault finding is key to a reliable home heating system. Regular maintenance, like an annual boiler service, can often prevent problems before they occur. By taking a logical approach, you can understand exactly why your heating has stopped and ensure it is fixed properly.
At Premier Gas, our heating engineers serving the North East have decades of experience solving complex heating issues with care and precision. We focus on identifying the root cause quickly, saving you time and giving you lasting peace of mind. To get your home back to its best, book an expert diagnostic inspection with our skilled heating engineers toda